
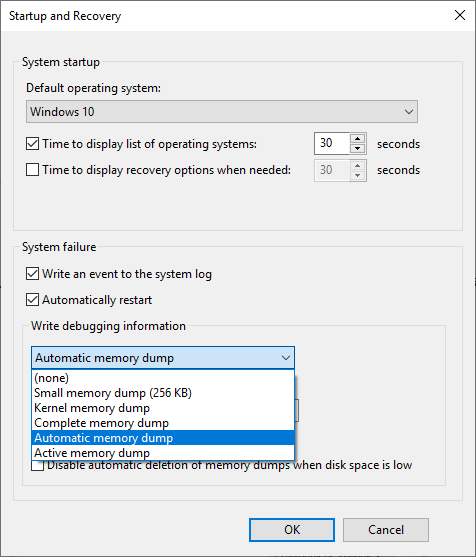
The WinDbg even makes an excellent job describing the crash in a language anyone can understand (The user manually initiated this crash dump).Moreover, the blue blocks with those files confirm that those files are dump files and you can easily identify among other files. The result points out that this was a manually initiated crash with an "e2" error code, which is correct since, for the purpose of this guide, we use these instructions to force a BSoD. For example, this test dump file shows the info of a Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) – also known as a bug check –. The information will be different depending on the problem.
Search for WinDbg, right-click the top result, select the Run as administrator option. To open and analyze a dump file created by a crash on Windows 10, use these steps: Once you complete the steps, the application will install, and it will be available through the Start menu. Click the Get (or Install/ Open) button.To install the WinDbg tool on Windows 10, use these steps: On Windows 10, you may find multiple ways to open and review a dump error file, but the easiest way is to use the WinDbg tool available through the Microsoft Store. How to open dump file with WinDbg on Windows 10 In this Windows 10 guide, we will show you the steps to open a dump file to try to figure out what caused the crash to resolve the problem on your computer. WinDbg (Windows Debugging) is a tool that has been designed for debugging kernel-mode and user-mode code, examining processor registries, and analyze crash dumps. The ".dmp" file includes the stop error message, list of the drivers loaded at the time of the problem, and kernel, processor, and processes details, as well as other pieces of information depending on the type of dump file you are using.Īlthough Windows 10 creates dump files automatically, the only problem is that you won't find any built-in tools to open them, and this is when the Microsoft WinDbg tool comes in handy. On Windows 10, every time there is a crash, the system creates a "dump" file containing the memory information at the time of the error that can help determine the reason of the problem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
